In the realm of skincare treatments, chemical peels have emerged as a popular and effective method for achieving a radiant and youthful complexion. Chemical peels are non-invasive procedures that utilize specially formulated solutions to exfoliate the skin, encouraging the shedding of dead cells and promoting new, healthier skin growth.
Read on to discover the benefits and process of chemical peels, shedding light on why they have become a sought-after option for rejuvenating and revitalizing the skin.
Table of Contents
Understanding Chemical Peels
This unique skincare treatment involves applying a chemical solution to the skin’s surface. The solution works to remove damaged and dead skin cells, stimulating the skin’s natural healing process. As the old skin peels away, new, fresher skin emerges, resulting in a smoother, more even complexion.
The History of Chemical Peels

The concept of chemical peels can be traced back thousands of years, with evidence of various forms of skin exfoliation and rejuvenation practices being used by ancient civilizations. The use of natural substances to improve skin appearance and treat various skin conditions has evolved over time, leading to the development of modern chemical peels as we know them today.
Ancient Civilizations
Ancient Egyptian, Greek, and Roman civilizations were among the earliest to experiment with skin treatments using natural substances. These cultures recognized the benefits of exfoliation and used various ingredients, including milk, wine, and natural acids, to achieve smoother skin and address certain skin conditions.
19th Century
The concept of chemical peels began to take shape in the 19th century. A Hungarian physician named Ferdinand Ritter von Hebra was among the first to use chemical substances, such as phenol, to treat skin conditions. He observed the regenerative effects of phenol on the skin, noting its ability to improve skin texture and reduce scars.
Early 20th Century
In the early 20th century, the use of chemical agents for skin treatments continued to evolve. Dermatologists and physicians experimented with various chemicals and concentrations to determine their effectiveness and safety. Pioneering dermatologist Dr. Unna, known as the “father of chemical peels,” contributed to the advancement of peeling techniques using trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and phenol.
1960s and 1970s
During the 1960s and 1970s, chemical peels gained popularity in the cosmetic and medical fields. The development of new chemical agents and advances in medical technology allowed for more precise and controlled peeling procedures. Phenol peels, in particular, gained recognition for their ability to address deep wrinkles and scars effectively.
Late 20th Century
Throughout the late 20th century, chemical peels continued to be refined and widely adopted by dermatologists and cosmetic practitioners. Glycolic acid, a type of alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), emerged as a milder and more accessible option for superficial peeling. This allowed for more frequent treatments and expanded the use of chemical peels to a broader range of patients.
Present day
In the 21st century, chemical peels have become a common and well-established skincare treatment. With advancements in medical science and technology, chemical peels are now safer, more precise, and offer customizable options to address specific skin concerns.
Today, chemical peels are used to treat a variety of skin conditions, including wrinkles, hyperpigmentation, acne, and uneven skin tone, in calming and relaxing settings such as the Dermani Medspa facility.
Types of Chemical Peels

There are various types of chemical peels, classified based on their depth of penetration and the specific skin concerns they target:
Superficial Peels
These peels are the mildest and mainly target the outermost layer of the skin (epidermis). They are effective in treating minor skin issues like uneven skin tone, light acne scars, and fine lines. Common ingredients used in superficial peels include alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs).
Medium Peels
These penetrate deeper into the skin, targeting the outer and middle layers (epidermis and dermis). They are effective in addressing moderate sun damage, age spots, and deeper wrinkles. Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) is a commonly used ingredient in medium peels.
Deep Peels
Deep peels reach the deeper layers of the skin, addressing severe skin issues like deep wrinkles, significant sun damage, and certain types of scars. Phenol is a potent ingredient used in deep peels, and this type of peel requires a longer recovery time.
Benefits of Chemical Peels
Exfoliation and Skin Renewal
Chemical peels promote exfoliation by removing dead and damaged skin cells. Doing so reveals fresh, new skin underneath, resulting in a smoother and more radiant complexion.
Improving Skin Texture
By encouraging collagen production and skin cell turnover, chemical peels can improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and acne scars.
Reducing Hyperpigmentation
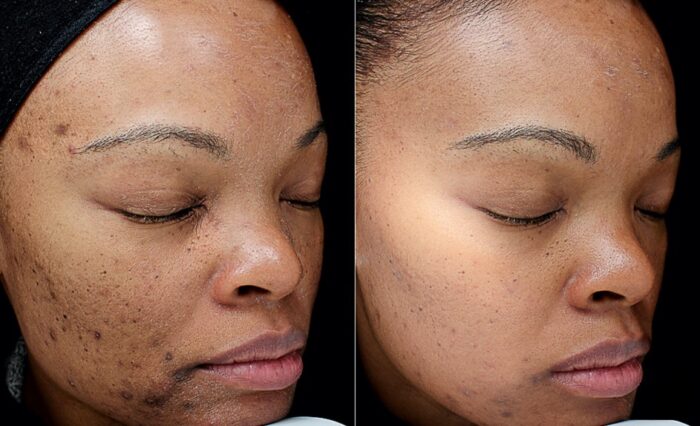
Chemical peels can effectively target hyperpigmentation, including age spots, sun spots, and melasma, resulting in a more even skin tone.
Treating Acne and Acne Scars
Superficial and medium peels can help manage acne breakouts and reduce the appearance of acne scars.
Boosting Skincare Product Efficacy
By removing dead skin cells and unclogging pores, chemical peels can enhance the absorption and effectiveness of skincare products applied after the treatment.
The Chemical Peel Process
- Consultation: Before undergoing a chemical peel, it is essential to have a consultation with a qualified skincare professional. During this consultation, the skin will be assessed, and the appropriate type of peel for the specific skin concerns will be determined.
- Preparation: Depending on the type of peel, the skincare professional may recommend a pre-peel skincare regimen to prepare the skin and ensure optimal results.
- Application: The chemical peel solution is applied to the cleansed skin. The specific duration of the application depends on the type and strength of the peel.
- Neutralization (if applicable): Some peels require neutralization to stop the chemical reaction once the desired depth of exfoliation is achieved.
- Post-Treatment Care: After the peel, the skin may appear red and feel slightly sensitive. It is crucial to follow the post-treatment care instructions provided by the skin care professional to aid in the healing process.
Conclusion
Chemical peels offer a plethora of benefits for individuals seeking to revitalize their skin and address various skin concerns. From superficial to deep peels, these treatments can be tailored to suit individual needs, delivering smoother, brighter, and more youthful-looking skin.
However, it’s vital to consult with a skincare professional to determine the most suitable type of peel and ensure the procedure is performed safely and effectively. With the transformative power of chemical peels, achieving radiant and glowing skin has never been more attainable.

