The human brain, the seat of all our experiences, emotions, and behaviors, is remarkably plastic. It evolves and adjusts to the stimuli it receives. One powerful stimulant, that has sparked debates across the world, is pornography. With the dawn of the digital age, it’s become more accessible, and its effects on our cerebral processes have raised questions and concerns.
In this piece, we will delve into the intricacies of how all the modern pornography content like my fav sex cams interacts with our neural pathways, highlighting both its physiological and psychological implications.
Table of Contents
Neural Mechanisms of Sensation
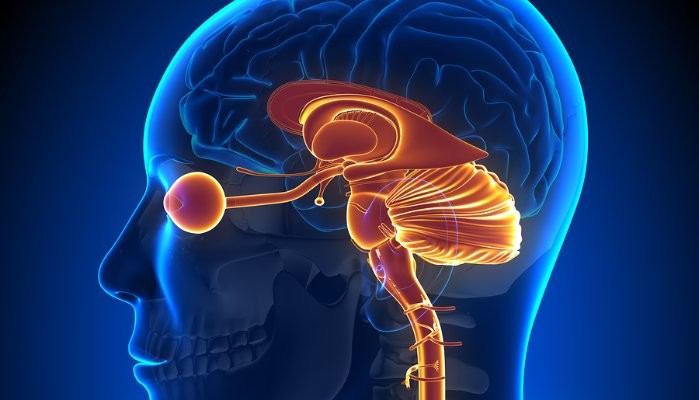
Every time an individual engages with explicit content, a symphony of neural events unfolds. The amygdala, responsible for emotional processing, lights up. It feeds information to the hypothalamus, which controls hormones and consequently, physiological reactions. This chain reaction underpins the immediate responses one feels.
The insula, a part of the cortex involved in the feeling of bodily sensations, is also activated. It plays a critical role in translating the explicit scenes on screen into tangible sensations. When synced with the thalamus, which processes sensory information, an individual doesn’t just ‘see’ the explicit content but ‘feel’ it.
Lastly, the anterior cingulate cortex gets into the mix. As a region linked with impulse control, its reduced activity during pornography consumption is notable. This dampening might explain the impulsive behaviors some exhibit after consuming adult content.
Dopamine and Reward Pathways

Dopamine, often dubbed the ‘feel-good’ neurotransmitter, surges when consuming adult content. It’s this chemical that makes the experience pleasurable. The brain’s ventral tegmental area releases dopamine, which then travels to the nucleus accumbens, signifying reward.
Over time, with regular consumption, this pathway can become hyperactive. The brain starts to associate the images on the screen with pleasure, almost similar to how it reacts to drugs or other addictive substances. This constant hit of dopamine creates a craving, urging the individual to return for more.
As the body craves more dopamine, tolerance levels rise. This requires viewing more explicit or novel material to achieve the same high. The repeated overload of dopamine not only intensifies cravings but could lead to a downregulation of dopamine receptors, rendering regular pleasures pale in comparison.
The Role of Visual Stimulation
The human brain has always been visually oriented. Almost half of our cerebral cortex is committed to processing visual information. Pornography capitalizes on this trait, offering vivid and graphic visuals that ensure attention is captivated.
Variation is a key aspect. The multitude of scenarios and actors ensures the brain is continuously receiving ‘new’ visual stimuli. This constant novelty intensifies arousal, as unpredictability is biologically engaging.
Such heightened visual stimulation, however, doesn’t come without repercussions. Consistent exposure can cause the brain to prioritize these hyper-aroused states, making everyday visual experiences seem mundane. This shift can hamper an individual’s ability to find pleasure in regular, non-explicit visuals.
Impact on Sexual Satisfaction
Engaging with explicit content can initially boost libido. However, over time, this can shift. With the brain becoming accustomed to the heightened stimuli of pornography, real-world intimate encounters may start to pale in comparison.
Given the unrealistic portrayal of intimacy in such media, users may develop skewed perceptions of real-life intimacy. This could lead to dissatisfaction, as reality might not match the on-screen fantasy.
Moreover, consistent exposure can result in performance anxiety. As the brain becomes conditioned to specific visuals and scenarios, the pressure to recreate them can be overwhelming. This could hamper genuine intimate moments and connections.
Addiction and Pornography

Not everyone who consumes explicit content becomes addicted. However, for some, the neural responses are so intense that they can mirror substance addiction. The dopamine-driven reward system gets so entwined with the explicit imagery that it becomes a compulsive need.
The repeated use of such media can lead to desensitization. This means that over time, individuals need more explicit or varied content to achieve the same dopamine high. This increasing dependence can disrupt daily routines and relationships.
For those who do become addicted, withdrawal symptoms are real. They can experience mood swings, irritability, and anxiety when trying to reduce or quit consumption. This further exemplifies the powerful grip pornography can have on the brain.
Neuroplasticity and Habituation

The human brain is adaptable. The more we indulge in a particular activity, the stronger the neural connections associated with it become. This principle, known as neuroplasticity, plays a role in habitual pornography consumption.
Over time, the brain starts weaving these strong neural patterns, associating pleasure with explicit content. This repeated behavior reinforces the neural pathways, making the act of viewing pornography a hard-to-break habit.
Yet, there’s a flip side. Habituation, the brain’s process of reducing responsiveness to unchanging stimuli, kicks in. This means that the same material might not bring as much pleasure over time, pushing individuals to seek more extreme content.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Beyond neurology, the emotional ramifications of consuming adult content are significant. Some individuals might experience guilt, shame, or anxiety post-consumption, especially if it conflicts with their personal or cultural beliefs.
As explicit media often portrays unrealistic standards, it can sow seeds of insecurity. Users might question their desirability, comparing themselves unfavorably with on-screen actors.
Notably, the isolation associated with consuming pornography can lead to loneliness. As the brain gets its dose of faux intimacy, the drive to seek genuine human connections might diminish, leading to an emotional void.
Gender Differences in Brain Responses

Men and women often differ in their neural responses to explicit content. Research indicates that men are more visually stimulated, with regions associated with visual processing showing heightened activity.
Women, on the other hand, might have more regions associated with memory and emotional processing activated. This suggests that women could be more focused on the narrative or emotional context.
These variations aren’t absolute and there’s significant overlap. But it does hint at the diverse ways our brains engage with explicit media, influenced by both biology and societal conditioning.
Ethical and Societal Considerations
The production and consumption of explicit content aren’t just biological affairs; they intersect with ethics and society. Many argue that pornography propagates harmful stereotypes, objectifies individuals, and sometimes is entangled with non-consensual acts.
There’s a pressing need to discern between consensual adult entertainment and content produced through exploitation. The latter can have severe repercussions on those involved, and viewers indirectly support this.
On a societal level, the normalization of unrealistic portrayals might lead to skewed perceptions of intimacy, consent, and mutual respect. Ensuring ethical consumption is a shared responsibility.
Final Thoughts
The dance between the brain and pornography is intricate. Understanding this dynamic aids in forging a balanced relationship with such media. In this digital age, where explicit content is just a click away, knowledge truly is power. Through informed choices and societal discussions, we can ensure that we’re in control, not our primal instincts.

